 Options on futures have come of age. In fact, at some exchanges, options trading outstrips growth in futures trading by a 2:1 margin. But this growth has a major flaw: Many people use options for the wrong reasons. Sound options trading begins with understanding basic concepts and dispelling common misconceptions about he potential benefits and limitations of these instruments.
Options on futures have come of age. In fact, at some exchanges, options trading outstrips growth in futures trading by a 2:1 margin. But this growth has a major flaw: Many people use options for the wrong reasons. Sound options trading begins with understanding basic concepts and dispelling common misconceptions about he potential benefits and limitations of these instruments.
The Basics - An option contract gives you the right to buy or sell something at a set price for a limited amount of time or at a specific future date. Options are common in many businesses, such as real estate, where an investor might purchase an option that will give him the right to buy a parcel of land at an agreed upon price for a six-month period, regardless of fluctuations in the market price of the land.
Options on futures are no different. A trader can buy an option in June allowing him to buy December T-bond futures at 100.00, even if the market price in December is 105,00. The buyer pays a price for this opportunity, called the premium. The option buyer is sometimes called the writer.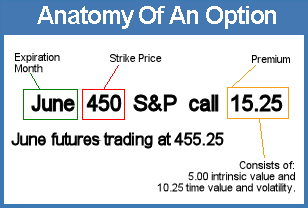
There are two kinds of options: calls and puts. A call option gives the owner the right to buy futures at a specific price; a put option gives the owner the right to sell futures at the specific price. This predetermined price is called the exercise price, or strike price. A call option owner who "exercises" his right becomes long futures, while an option seller is "assigned" a short futures position. When a trader sells an option, he risks having a losing futures position at any time. In return for assuming this risk, he receives the option premium.
The owner, on the other hand, is under no obligation to exercise, and may sell the option or hold it through the term of the agreement. The last day a buyer can exercise an option is called the expiration date, which is established by the exchange. For example, the owner of a March 445 S&P call call buy March S&P futures at 445.00 until March 17, if he so chooses. The option expires at the end of trading on this day.
Most listed options in the United States are American style options, which allow the holder to exercise any time up through expiration day. European style options can be exercised on expiration day only.
Ins and Outs - The strike price of an option can be described three ways:
In-The-Money refers to calls with strikes prices below the current market price of the underlying future and puts with strike prices above the market price. If coffee futures are trading at 195.00. a 194.00 call is in-the-money, as is a 196.00 put.
At-The-Money options are calls and puts with strike prices equal to the current futures price. If coffee is 197.00, both 197.00 coffee calls and puts are at-the-money.
Out-Of-The-Money refers to calls with strike prices above the current futures price, and puts with strike prices below the future price. With coffee at 194.00, a 195.00 call and a 193.00 put would both be out-of-the-money.
With March bonds at 100.22, the owner of a March 98.00 call could exercise his option, become long bond futures at 98.00, sell the futures at 98.00, sell the futures and make 2.22. If the trader paid less than 2.22 for the opions, he would make a profit on the trade.
Because option buyers are not required to exercise, their market exposure is limited to the premium paid for the option. For sellers, however, risk is equivalent to an outright futures contract, because they can be assigned a futures position at any time.
