Many traders, especially those who have not traded very long, find trending declines very difficult to trade. Many trading and analytical tools which perform well in uptrends, or even in sideways patterns, often perform differently in downtrends. This is not to say such tools will not work well in a downtrend, but, realistically, many perform differently.
Many traders, especially those who have not traded very long, find trending declines very difficult to trade. Many trading and analytical tools which perform well in uptrends, or even in sideways patterns, often perform differently in downtrends. This is not to say such tools will not work well in a downtrend, but, realistically, many perform differently.
Many traders (once again, especially those with little experience) tend to be biased to the long, or buy, side of the market. Such traders often have difficulty adapting to the changes which may occur in the performance of their favorite tools in declining markets. Thus, many tend to shy away from the short side of markets. This is unfortunate as markets often fall more quickly than they go up. As a result, profits can be potentially harvested faster in a down move than in an uptrend.
While some traders tend to avoid the short side of markets altogether, others would be interested in selling short if only they could find a way to get on board trending declines. As mentioned earlier, while many tools don't appear to work as well in a down- trend, there is a pattern which occurs often enough to be helpful in analyzing and trading.

The reliable pattern which often develops within down trending moves is a consistency of the upward reactions. The consistency within upward reactions can be in terms of time or price or both. However, most patterns tend to involve time, either alone or in combination with price.
Generally speaking, upward reactions in true downtrends tend to last from 1 to 3 days. The reactions are not limited to 3 days; however, many declines will follow this pattern.
To be more specific, individual markets often mark the maximum time span of most upward reactions with the first rebound in a downtrending pattern. For example, if the first upward reaction lasts two days, many of the subsequent rebounds within the downtrend will last two days or less. A good example of this phenomenon occurred in the February/March, 1991 collapse in the currency markets.
The first rebound in the Swiss franc, following the posting of the February high, lasted for about a day and a half. From that point forward until the primary downtrend came to an end in late March, no upward reaction (arrows) lasted much more than a day and a half. And, when the Swiss franc rebounded for more than a day and a half, (circle) it proved to be a signal the clean portion of the downtrend had come to an end.
The trading strategy is quite simple. In general, traders may look to sell 1- to 3-day rebounds in downtrending markets. If a reaction lasts longer than the longest previous reaction, the strategy then moves to either being stopped out or to look for a gracious way to move to the sidelines on the next break. This is done because, even if the market eventually moves lower, what remain, compared to the previous trending portion or "meat" of the move, often prove to be the "crumbs." Obviously, the strategy is adjusted when a specific market has marked its reaction time.
The spring, 1991 situation in the new-crop corn market pres- ents an example of a time span longer than three days being marked as the primary reaction time. After collapsing from the March high, December corn marked its key reaction time with the sharp rebound into early April. This 4-day bounce set the stage for subsequent reactions to last from 1 day to 4 days. In addition, December corn has marked the likely size, in terms of price, of most subsequent reactions.
The rebound posted in December corn into early April was 13.25(E. This is likely to be the approximate size of the largest subsequent rebound which occurs within the downtrending move. A rebound which is substantially larger than 13.25 cents is likely to signal an end of the primary decline. However, on a daily degree, it is rather obvious that a 13.25C rebound in corn is a large reaction. While a 4-day reaction time is realistic, most reactions in price are likely to be smaller than 13.25 cents.
Notice the 4-day rebound which followed the posting of the April high. This upward reaction was 5cents. From this point on, it was/is reasonable to expect most reactions to be in the neighborhood of 5(t or Go; and to last from 1 to 4 days. However, it would be wise to allow for at least one larger-degree rebound of about 13 cents.
In the spring, 1991 situation in the December corn market, a possible trading approach would be to sell rebounds from a new low of 5cents to 6cents. Risk could be limited to a point which is 14cents or 15cents above a new low. Thus, the effective risk should be about 8cents to l0cents. Once a new low is posted, if one were using "tight" stops, the risk could be limited to about 7cents to 8cents above each new low. Otherwise, a 14cent or 15cent trailing stop above each new low should keep one in position for the bulk of a move. While this is a possible approach, it is not necessarily a specific or the only approach to trading a short position.
As always, knowing the personality of a market can prove beneficial. In the spring, 1991 corn market, it was wise to allow for one rebound in time of up to ten days. This is due to the presence of such rebounds in time in potentially similar previous downtrends in the corn market.
The tendency for consistent reactions in a downtrend should be an attractive addition to one's technical "toolbox". This pattern offers a low-risk method to reap potentially substantial rewards.
 There are four components to an options price: underlying contract price, intrinsic value ( determined by strike price), time value (time remaining until expiration) and volatility. (A fifth element, interest rates, also can affect option prices, but for our purposes is unimportant.)
There are four components to an options price: underlying contract price, intrinsic value ( determined by strike price), time value (time remaining until expiration) and volatility. (A fifth element, interest rates, also can affect option prices, but for our purposes is unimportant.)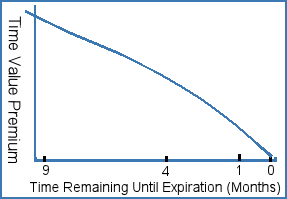



 Join Susan and Jeremy today LIVE at 5:00 ET to learn the ins and outs of trading. Whether you're a beginner, or just want to refresh your already established skills, tonight's show is for you. It will include demonstrations regarding trading strategies and how to incorporate those strategies when trading Stocks, Forex, and Futures. It will also show you how to enter and exit a trade using MarketClub's "Trade Triangle" technology. Of course, you will have to tune in for the full, detailed lesson. You might even learn something new!
Join Susan and Jeremy today LIVE at 5:00 ET to learn the ins and outs of trading. Whether you're a beginner, or just want to refresh your already established skills, tonight's show is for you. It will include demonstrations regarding trading strategies and how to incorporate those strategies when trading Stocks, Forex, and Futures. It will also show you how to enter and exit a trade using MarketClub's "Trade Triangle" technology. Of course, you will have to tune in for the full, detailed lesson. You might even learn something new!